As the number and severity of cybersecurity attacks rise each year, organizations are compelled to look for measures to protect sensitive data. The abundance of cybersecurity solutions on the market may create confusion and pressure, as choosing the wrong one may lead to security gaps. Many companies turn to data loss prevention (DLP) systems, since they have been on the market for years.
But is a DLP system enough to protect your data? Can we consider these time-tested solutions a panacea against all cybersecurity incidents? Stay with us to find out. In this article, we outline the main pros and cons of DLP systems and explain how to cover their potential security flaws if you decide to deploy one.
What is a data loss prevention (DLP) system?
Data loss prevention, or data leak prevention, is the process of using different tools and practices to mitigate the risks of data-related security incidents. Data loss prevention benefits organizations by helping them detect and prevent sensitive data loss, leaks, exfiltration, and breaches.
Data loss prevention (DLP) describes a set of technologies and inspection techniques used to classify information content contained within an object — such as a file, email, packet, application, or data store — while at rest (in storage), in use (during an operation) or in transit (across a network).
Gartner
A DLP system, in turn, is a software solution or a set of tools that can help prevent the loss of data. DLP systems monitor sensitive data to detect and block suspicious operations with it inside an organization’s infrastructure.
Frequently implemented to combat insider threats, DLP solutions are also a requirement of many industry security standards, laws, and regulations, such as GLBA, DSS, SOX, and FISMA.
DLP solutions can help prevent the following types of data security incidents:

A data breach is a security incident involving unauthorized third-party access to an organization’s critical data. Cybercriminals typically breach an organization’s security to sell sensitive data. Data breaches can be carried out using various methods such as social engineering, malware, and hacking.
Data exfiltration is the unauthorized and intentional transfer of critical data out of an organization’s perimeter. Also referred to as data theft, exfiltration is mostly done by malicious insiders acting as authorized employees.
A data leak, or data leakage, is an unauthorized but unintentional transmission of sensitive data from an organization’s perimeter. Leaked sensitive data may be exposed publicly or used maliciously by third parties to perform a cybercrime such as identity theft.
Data loss is any event or process that leads to data being corrupted, damaged, or completely destroyed, and therefore inaccessible or unusable.
Note: The above data security categories are similar and frequently overlap. Some classifications take data loss as an umbrella term covering all of the above-mentioned data security incidents. Note: The above data security categories are similar and frequently overlap. Some classifications take data loss as an umbrella term covering all of the above-mentioned data security incidents.
DLP systems may consist of various software means to protect sensitive data. Standard measures include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software, which mainly focus on external attacks that may cause data loss. More advanced measures comprise machine learning, user activity monitoring, and other technologies to detect unauthorized access and malicious insider activity.
In our analysis of DLP systems, we focus on those specifically designed to prevent unauthorized attempts to copy, modify, delete, or send sensitive data.
Auditing and Reporting with Syteca
How does a DLP system work?
To understand how DLP solutions operate, let’s take a closer look at their core workflow. Each organization’s DLP system is slightly different; however, all of them share similar key steps:
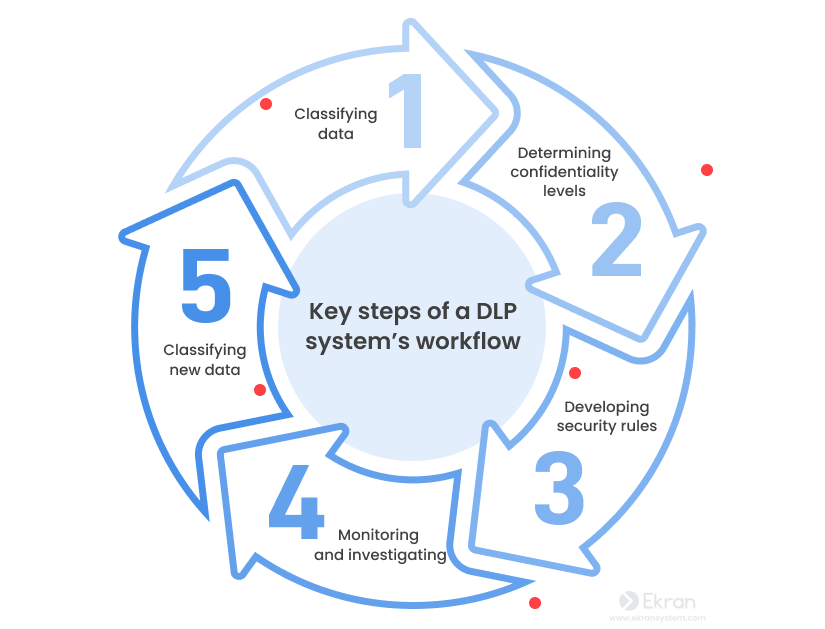
1. Classifying data. Cybersecurity experts use a DLP solution to sort and label every piece of data in an organization’s infrastructure with a particular classification level, such as public, sensitive, or internal. Classification is a lengthy and complex process that requires the development of data classification policies. It may be manual or automated, depending on the DLP solution in place.
2. Determining confidentiality levels. Based on the classification results, security officers assign specific phrases indicating confidentiality levels to different types of data: private, confidential, top secret, credit card information, etc. Depending on the company, there could be hundreds or even thousands of confidentiality markers.
3. Developing security rules. Once all of the organization’s data is processed, a cybersecurity team configures the DLP system’s behavior by creating rules. These rules define how the system responds when a specific confidentiality marker is triggered: by sending an alert notification, stopping transmission of confidential data, or revoking the user’s access rights.
4. Monitoring and investigating. The system begins monitoring sensitive data after the security rules are set up. When an alert is triggered, the system responds to the event as configured and notifies the cybersecurity team. Security personnel then analyze the event to see if it is an incident or a false positive.
5. Classifying new data. As fresh data enters the organization’s infrastructure, the DLP process starts all over again, beginning with the classification step. Some DLP solutions can offer a certain level of automation, but it’s not flawless – it may leave gaps in security and affect your organization’s workflow.
Types of DLP systems
Depending on the environment they operate in, we can distinguish the following types of DLP solutions:

Key DLP system features
The technical capabilities of modern DLP systems vary, but certain DLP solution features are critical to thoroughly protect data. Here are the key features DLP systems should have:

Data identification
A DLP system needs to determine what data requires protection the most. This can be determined manually or automatically. DLP systems either identify sensitive data with the help of machine learning or enable users to define sensitive data manually by applying rules or categories.
Protection of data at rest
DLP systems can protect data located in various types of storage within your network, including databases, software applications, cloud repositories, computers, and mobile devices.
Protection of data in motion
Malicious actors may exploit your organization’s data movements to reroute data. DLP systems can protect data in motion and detect cases when data is moved in violation of data security policies.
Data leak detection
DLP solutions have the ability to identify anomalous or suspicious actions performed with the organization’s data and alert security officers about possible data leaks.
Now that you know more about DLP systems, let’s consider their pros and cons.
Advantages and disadvantages of DLP systems
This section will help you determine whether DLP solutions are worth your attention. By comparing the main advantages and disadvantages of DLP systems, you’ll be able to make the right decisions about protecting sensitive data in your organization.
Take a look at our key findings:

Let’s explore these pros and cons of DLP systems in greater depth.
Key benefits of DLP systems
A DLP solution benefits your cybersecurity system and enables your organization to:
- Prevent data-related incidents caused by insiders
Most DLP systems are good at protecting data inside an organization’s perimeters. By classifying and constantly monitoring sensitive information, DLP solutions can easily detect and prevent suspicious and unauthorized operations with data. DLP systems can also detect unintentional and accidental actions that may cause data loss and leaks.
- Comply with cybersecurity requirements, laws, and standards
As mentioned earlier, some organizations employ DLP solutions to comply with relevant data protection standards, laws, and regulations such as HIPAA, GLBA, PCI DSS, SOX, and FISMA. Although they do not cover all IT requirements on their own, DLP tools can help you reduce the risks of non-compliance and extensive fines.
- Improve visibility and control over the organization’s data
DLP systems provide companies with visibility into what sensitive data they have and what’s going out of the building. The control over data that DLP solutions provide can empower organizations to select the level of confidentiality for each record and configure how the system reacts to signs of data security incidents. With a DLP system in place, you can see who’s trying to send out information and possibly stop a data breach before it can cause too much damage.
- Definitively authenticate each user before data is accessed
DLP solutions can prevent suspicious attempts to copy or send sensitive data by checking whether the user is authorized to do so. Authentication is also important to validate users’ identities and prevent malicious access to critical assets. However, many DLP systems need external identity and access management solutions to work properly.
User Activity Monitoring with Syteca
Major downsides of DLP systems
Deploying a DLP system in your organization to prevent data-related incidents might sound like a good idea. However, there’s a risk of DLP software leaving gaps in your corporate security if there are no other cybersecurity measures in place.
When choosing a DLP solution, watch out for the following:
- Disrupt business processes and decrease employee performance
When misconfigured, DLP systems may compromise the operation of network systems, reduce employee performance, and generate false positives. Even a well-configured DLP system cannot guarantee that important data will not be held hostage in vain. Security teams frequently decide to loosen DLP security rules due to constantly disturbed employees, making data vulnerable to cybersecurity threats.
- Rigidness and limitations of common DLP solutions
Most DLP systems are quite futile when it comes to cybersecurity incidents not related to data operations. Such systems are also ineffective when data travels outside the controlled environment, such as an employee’s personal laptop. In addition, the implementation of a DLP solution can impose certain restrictions on other software in your organization. New versions of some applications may interfere with your DLP environment, so you might even have to postpone upgrades, increasing the risk of zero-day exploits.
- Complex configuration and management
Your security teams may spend hours and even days setting up the DLP system for it to work properly and create fewer false positives. The data classification procedure is the most critical and difficult stage of a DLP system’s workflow with many stumbling blocks. Automating this process may result in misclassifying sensitive data, while manual classification is lengthy and prone to human errors. Even well-configured DLP solutions require regular maintenance and time-consuming adjustments, distracting your security team from other important tasks.
- Need for additional software
Designed solely for monitoring data, DLP systems overlook other essential aspects of cybersecurity, such as access management, identity management, and insider threat management. This creates a necessity to install supplementary software:
- User activity monitoring solutions
- Access management controls
- Authorization and authentication tools
Malicious insiders are the Achilles’ heel of DLP systems. A tech-savvy insider can learn the system’s behavior and come up with ways around it such as changing file types, saving files under different names, copy/pasting data, or taking screenshots.
Move on to the next section to learn how to enhance the ability of DLP solutions to protect sensitive data and mitigate their major weaknesses.
Privileged Access Management with Syteca
DLP solutions approach cybersecurity by classifying and monitoring sensitive data. However, effective data loss prevention requires a holistic approach. To achieve the best results, consider combining your DLP system with cybersecurity measures focused on users’ access and behavior.
This is where the Syteca can be beneficial. Syteca is an insider risk management platform that can help protect your organization’s sensitive data and systems from malicious activity of employees and third parties.
Syteca’s non-intrusive nature allows you to integrate its privileged access management (PAM) and user activity monitoring (UAM) capabilities into your cybersecurity program without interfering with your DLP system. Unlike many DLP solutions, Syteca is easy to deploy, configure, and manage and doesn’t affect your network, ensuring business process continuity and employee productivity.
Syteca is highly flexible and customizable, allowing for adjustments to meet your organization’s specific needs. In addition, Syteca can help you meet the requirements of many cybersecurity standards, laws, and regulations.
Syteca’s diverse functional complexity can help you protect sensitive data by empowering you to:
- Monitor and record user activity. Watch live and recorded user sessions of your employees and third parties in a video format. Coupled with helpful metadata such as visited websites, opened applications, and typed keystrokes, video records of user sessions allow for more visibility than simply monitoring operations with data, as you can see more signs of a possible insider threat.
- Granularly manage access. Get visibility over all accounts and control access rights of regular and privileged users in your system. You can leverage the principle of least privilege by limiting access to your organization’s critical assets. Syteca also allows you to provide users with one-time access and limit the time for which access is given.
- Secure users’ accounts. Verify users’ identities with two-factor authentication (2FA) and distinguish users of shared accounts. Syteca’s sophisticated password management capabilities can help you optimize secrets delivery, automate password rotation routines, and secure passwords in an encrypted vault.
- Export monitoring data. Generate and export recorded data using a collection of comprehensive and customizable reports. With Syteca, you can conduct internal audits and export evidence in a standalone protected format for cybersecurity investigations.
- Establish incident response. Get notified about potential cybersecurity threats promptly and respond to incidents manually or automatically by blocking the user, warning the user, or stopping the suspicious process. Syteca’s alert rules are based on a user’s behavior: visited websites, executed commands, launched applications, etc.
- Anonymize monitored data. Remove identity markers from the user activity monitoring results and protect your users’ personally identifiable information from accidental disclosure. When needed for thorough investigation, Syteca allows for de-anonymizing data per data protection officer approval.
Syteca’s AI-powered user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) module can enhance the incident response experience in your organization by comparing real-time user activity to baseline behavior. Instead of blocking an incident when it happens, UEBA allows you to catch early signs of an incident. For example, suppose an employee tries to access your system during non-working hours. In that case, the system will notify your cybersecurity team about suspicious activity and stop it, preventing potential account compromise or an insider attack.
By deterring, detecting, and disrupting insider threats in your infrastructure, Syteca can help enhance your DLP solution or serve your company as an independent cybersecurity defense against insider threats.
Insider Threat Management with Syteca
Conclusion
DLP systems can help protect data in your organization by constantly classifying and monitoring sensitive assets. However, by focusing on operations with data only, DLP solutions may leave certain aspects of cybersecurity uncovered, as there are multiple ways external attackers and malicious insiders can bypass DLP alert rules and remain unnoticed. To leverage the benefits of data loss prevention in your organization, consider pairing a DLP system with additional cybersecurity measures.
A full-cycle insider risk management platform like Syteca may be a powerful enhancement to your organization’s data cybersecurity. By monitoring the activity of all users in your IT infrastructure and managing their access rights, you can significantly reduce the risk of critical data loss, leaks, exfiltration, and breaches.